Oracle Interview Questions: Are you preparing yourself for an oracle interview? Are you wondering where you will get sample questions for guiding you on what to encounter during an interview? Don’t because we have a solution. This article contains a couple of questions that are likely to be asked. Studying and understanding these questions will offer you the confidence you need to pass the interview.
Top Oracle Interview Questions for Experienced
Q1-What’s Oracle?
Ans: This is a company and also a database server that manages information in a structured way. Oracle enables clients to keep & retrieve related information in a multiuser environment. This allows several users to concurrently access similar information. All this can be accomplished while providing high performance.
Q2-How can one differentiate between Varchar2 and Varchar?
Ans: Varchar and Varchar2 are Oracle data varieties that are utilized to keep character strings of variable length. Pointing out major variances between these
Varchar can keep characters for about 2000 bytes, varchar2 can keep characters of about 4000 bytes. Varchar will hold space for characters that are defined on declaration even if each of them isn’t used. Varchar2 will release unused space.
Q3-What’s a SYSTEM-tablespace & when it’s created?
Ans: When a database is made in an Oracle database system, it auto-generates a SYSTEM-named SYSTEM-tablespace. SYSTEM tablespace has information dictionary tables for one’s entire database.
Q4-What’s BCP or bulk copy in Oracle?
Ans: BCP or Bulk copy in Oracle is utilized to export or import information from tables & views though it doesn’t copy the structure of similar information data. The major benefits of BCP are a quick mechanism for coping information & one can take the information backup easily.
Q5-Explain the relationship between database, data file, and tablespace?
Ans: Oracle-database possesses a single or extra logical-storage unit known as tablespaces. Every tablespace at Oracle database contains one/more files known as datafiles. Tablespaces collectively keep the whole information of databases. Speaking about datafiles, these are the physical structure which confirms with operating-system as to which the Oracle-program is operating.
Q6-What’s Oracle View?
Oracle view refers to a virtual table. Each view has queries joined to it. A query is a SELECT-statement that pinpoints the columns & rows of a table(s) that the view utilizes.
Q7-What are different Oracle-database objects?
Ans: Tablespaces: It’s a logical storage-unit in Oracle.
Tables: It’s a set of elements that are organized horizontally or vertically.
Views: These are virtual-table gotten from a single or more table.
Synonyms: It’s a name given to tables.
Indexes: It’s a performance tuning-method to process records.
Q8-What the difference is between the TRUNCATE and DELETE commands?
Ans: All the commands are utilized to remove information from a database.
Differences between these 2 include
- TRUNCATE refers to a DDL-operation while DELETE refers to a DML operation.
- TRUNCATE command frees object storage-space while DELETE command doesn’t.
- TRUNCATE removes every row though leaves table-structure intact. It can’t be rolled-back as it provides COMMIT before & after command execution. DELETE-command can be moved back.
- DELETE is slower compared to TRUNCATE which is faster
Q9-What’s meant by RAW-datatype?
Ans: RAW datatype is utilized in keeping variable-length binary byte strings or data. The difference between VARCHAR2 & RAW datatype in PL/SQL doesn’t recognize the data kind & hence, can’t do a conversion when RAW information is moved to various systems. This information kind can just be inserted or queried in a table.
Q10-What’s constraint & how does one use it?
Ans: These are rules which you set up for information. These can be utilized either when creating a table or later or when altering the table.
Q11-What’s the difference between COALESCE & AGGREGATE?
Ans: AGGREGATE command assists in joining the values of numerous records to one value. COALESCE command takes back the value in the table set not null. Example; functions like sum, count, and average.
Q12-What’s ANALYZE command about Oracle?
Ans: It’s utilized in performing various purposes on tables, indexes or cluster. The list below specifies ANALYZE command usage in Oracle:
It’s used in validating object structure
It’s used to identifying migrated & chained rows of cluster or table
Helps in deleting statistics that are utilized by an object from an information dictionary.
Assist in collecting statistics about objects utilized by users & are kept on to information dictionary.
Q13-What’s a snapshot concerning the Oracle database?
Ans: This is a replica of the target master-table from one point-in-time. In other words, a snapshot is a duplicate of a table on a remote database.
Q14-What’s the save point concerning Oracle database?
Ans: These are utilized to dividing a transaction into smaller pieces. This also enables rolling-back of a transaction. A maximum of 5 save-points are enabled. It’s utilized in saving our information, every time one encounters a problem one can roll-back from a point where they saved their SAVEPOINT.
Q15-What are the kinds of joins that are utilized in writing subqueries?
Ans: Join is utilized in comparing & combining. It means join & return particular rows of information from 2 or extra tables in a database.
The three kinds of joins available in SQL are utilized in writing the sub-queries.
Outer Join: It helps in finding & returning matching information & some dissimilar information from tables.
Self Join: It’s a join where the table is combined with itself, particularly when a table has a foreign-key that references its particular primary key.
Equi-join: This is a join that has a join state containing an equivalence operator. Equijoin returns just the rows which have equivalent-values for particular columns.
Q16-What’s Oracle Index?
Ans: This is an optional-structure that’s associated with a table to have direct-access to rows, that can be made to increase the performance of information retrieval. An index is created on one/more table columns.
Q17-What’s Tablespace?
Ans: The database is separated into Logical Storage-Unit known as tablespaces. A tablespace is utilized to grouped related-logical structures together.
Q18-What’s Schema Object?
Ans: These is logical structures that directly bring up to database’s information. Schema-objects include tables, sequences, views, synonyms, clusters, indexes, database triggers, functions packages, database links, and procedures.
Q19-What’s RAW-datatype concerning Oracle?
Ans: RAW-datatype in Oracle is utilized in storing variable-length byte string or binary data values. Maximum-size for a raw to a particular table is 32767 bytes.
One may get confused when to operate with varchar2, varchar, and RAW. PL/SQL doesn’t recognize information type & hence, it can’t have conversions when RAW information is transferred to various systems. The information kind can just be queried or can be put on a table.
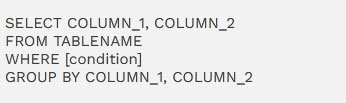
Q20-When does one use the GROUP-BY clause at SQL-Query?
Ans: GROUP-BY clause is utilized to identify & group information by one/more columns in a query result. The clause is normally utilized with aggregate tasks like AVG, COUNT, MIN, MAX, SUM, etc.
The Syntax is;
Q21-What’s the difference between pre-query & pre-select?
Ans: Pre-query triggers fire before a query is executed & fire once as one tries to query. With the assistance of a trigger, one can amend the where clause section dynamically.
Moreover, pre-select request fires during query execution & count-query processing after the Oracle creates construct. The select statement is issued, though before a statement is issued.
Remember that pre-query trigger-fires earlier than Pre-select trigger.
Q22-What are various kinds of synonyms?
Ans: The 2 kinds of synonyms/alias include:
Public: Can be retrieved by database user
Private: Can be accessed by the owner
Q23-What’s BLOB data kind in Oracle?
Ans: This is a data kind that has varying lengths of a binary string. It’s utilized to keep two gigabytes of memory. BLOB data kinds, the length requires to be stated in bytes.
Q24-What’s Logical backup concerning Oracle?
Ans: It’s utilized in reading a set of database records & writing them into files. The export utility is utilized in taking the backup while Import utility is utilized in recovering from backup.
Q25-What are recursive hints concerning Oracle?
Ans: This number of times a dictionary-table is recurrently referred to by several methods is understood as recursive-hint. Recursive-hint is happened because of the small size of the information dictionary cache.
Q26-What’s meant by Redo-Log file mirroring?
Ans: Mirroring is a method of having a copy of Redo-log files. It’s done via creating a group of log-files together. This offers that LGWR will auto writes them to every member of the current on-line redo log-group. Furthermore, if the group-fails, the database will auto switches over to the next group which diminishes performance.
Q27-What’s the data kind of DUAL table?
Ans: Dual-table is a single-column table that’s present in the Oracle database. Moreover, this table comes single Varchar2(1)-column known as Dummy that has some value of ‘X’.
Q28-What are the attributes of the Cursor?
Ans: Every Cursor at Oracle has some set of attributes that allows an application-program to check the Cursor state. Attributes can be utilized in checking whether the cursor is closed or opened, not found or found & also find-row count.
Q29-Which is the quickest query method that allows you to fetch information from the table?
Ans: The fastest query way of fetching information from a table is via using Row ID. A row can be gotten from a table with the help of RowID.
Q30-Explain the function of %TYPE & %ROWTYPE information kind with example?
Ans: %ROWTYPE & %TYPE are attributes available in PL/SQL that can inherit datatypes of tables that are defined inside a database. A major purpose of utilizing these attributes at Oracle is to offer information independence & integrity. Moreover, note that, if any datatypes get altered in a database, PL/SQL-code gets auto-updated including the alteration in datatypes.
%ROWTYPE: It’s used in defining a whole row of records with a similar structure to table structure.
%TYPE: It’s used in declaring a variable that requires one to have similar information kind as a table-column.
Conclusion
With this set of questions, I believe you will be in a position of answering them correctly when asked. Remember the way you present your answers in an interview matters a lot hence you need to stay calm and have confidence.
